Organizations are increasingly realizing the inherent complexities involved in transitioning their existing IT operations to comply with Department of Defense (DOD) cybersecurity rules, which are crucial for securing new contracts or renewing existing ones, regardless of the size of the DOD contracts relative to their overall business. Organizations are shifting to cloud-based secure enclaves to support controlled data environments and reduce the internal operational friction to transition all their IT operations that may not require full adherence to the compliance requirements. Controlled data environments refer to secure and regulated environments where sensitive and confidential data is handled.
Organizations that are leveraging Azure are finding the following benefits:
- Flexibility
- Automation
- Foundation for technology growth
- Support for multiple workload requirements
- Dev environments, testing, storage of applications
Defense Industrial Base (DIB) organizations working with DOD contracts and/or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) data are constantly dealing with cybersecurity requirements during contract renewals or when winning new contracts. These organizations need to provide an environment that addresses compliance requirements in contracts while delivering core services to stakeholders, businesses, or internal IT teams.
DIB organizations are utilizing Azure for controlled data environments as security and privacy concerns have become increasingly pressing. Data initiatives often involve sensitive and confidential data, and DIB organizations must ensure that their operational activities comply with regulations such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS), International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), and other cybersecurity requirements. Furthermore, contract sponsors, both government and private, now demand enhanced cybersecurity compliance requirements to be met before contracts are awarded.
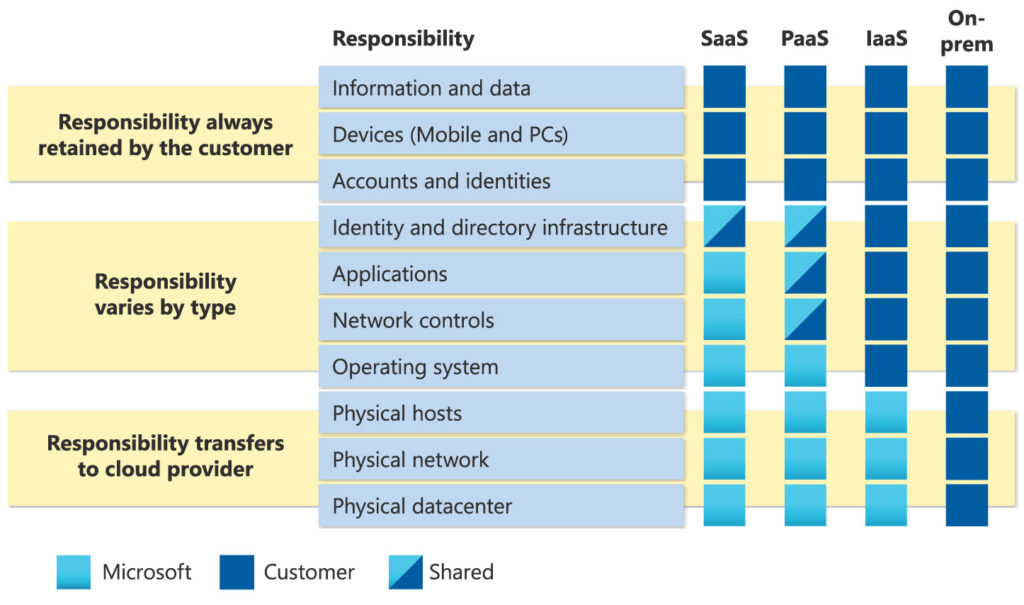
To address these challenges, DIB organizations can engage with controlled data environments in the cloud through an “as-a-service” model. In this model, IT teams can access the required computing, data storage, and platform services resources through a third-party service provider, eliminating the need to manage and secure these resources internally.
Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) like Microsoft have taken significant steps in enabling secure controlled data environments in the cloud. Microsoft Azure offers a comprehensive suite of cloud-based services for controlled data initiatives. These services provide IT and business stakeholders with access to high-performance computing resources, data storage, and data analytics capabilities, all of which are fully compliant with regulatory requirements when implemented correctly.
Another advantage of controlled data computing in the cloud is the ability to scale resources quickly and easily. In the traditional research computing model, acquiring additional computing resources can be a slow and complex process, often involving procurement, installation, and maintenance. However, with controlled data computing in the cloud, IT and stakeholders can quickly obtain additional resources as needed, allowing them to adapt to changing cybersecurity requirements and maximize their business outcomes.
In conclusion, controlled data environments in Azure Secure Enclaves can provide DIB organizations with a powerful and flexible solution for their cybersecurity and business initiatives. By engaging in an “as-a-service” model, organizations can obtain access to the required resources in a compliant and secure manner, freeing up internal IT teams to focus on other critical initiatives and enabling stakeholders to leverage the advanced capabilities of the cloud to advance their controlled data initiatives. The benefits of leveraging Azure include flexibility, automation, a foundation for technology growth, and support for multiple workload requirements, such as development environments, testing, and storage of applications.

